Antidepressant Guidance
Test Description:
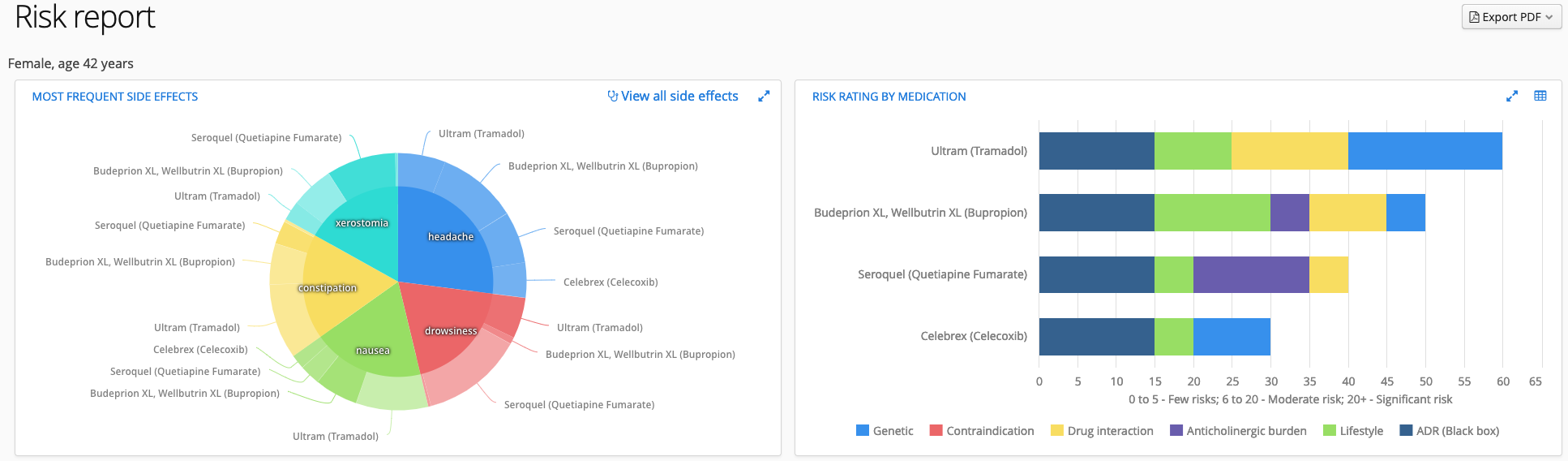
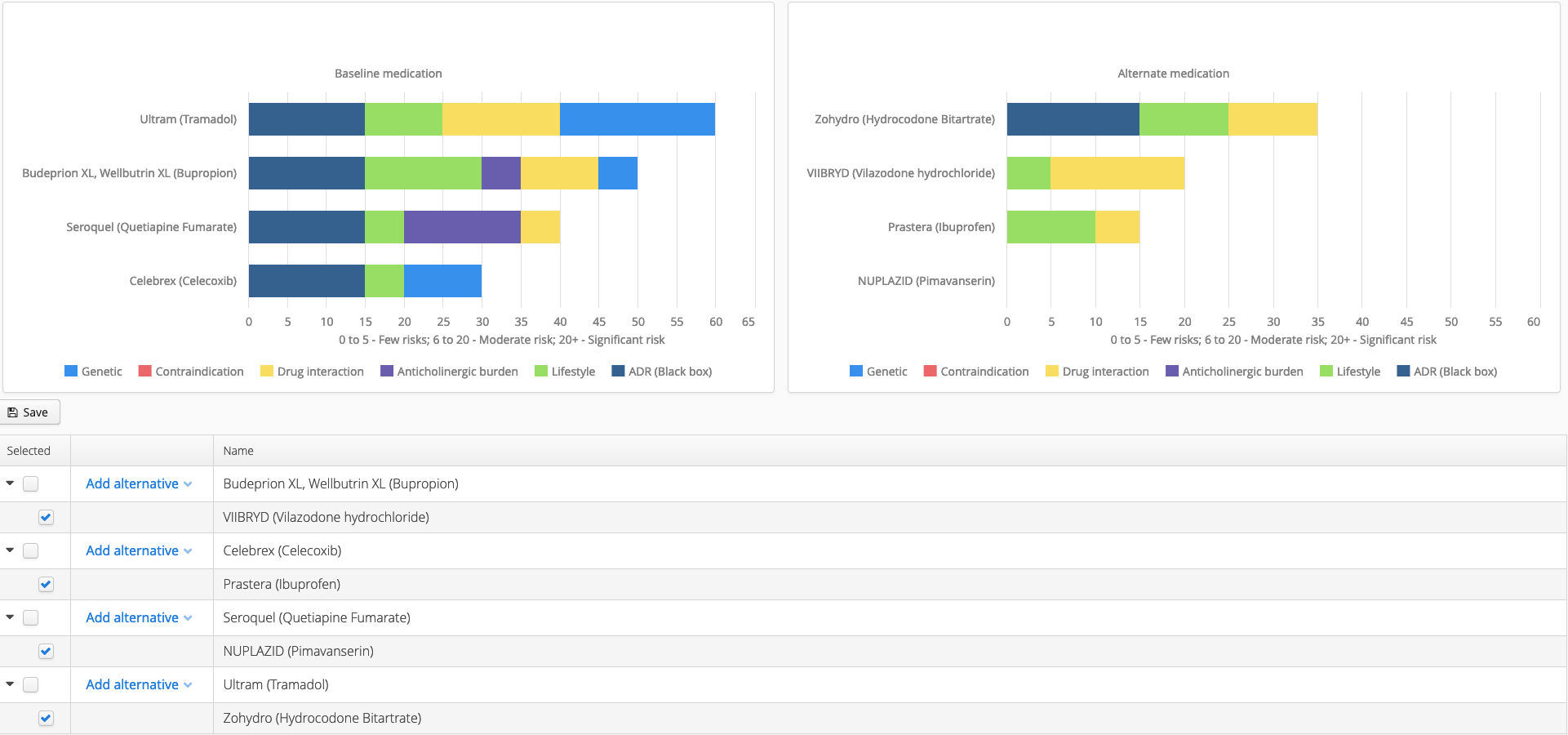
AMPLIS is best in class pharmacogenetic guidance for Anti-Depressant selection. RCT1 and concordance2 studies both indicate Amplis may greatly increase remission rates with first drug selected through the proprietary combinatorial algorithm based on the understanding of Auto-Binding Cassette and Uridyl-Glucuronosyltransferase systems. In addition to the power of this algorithm, AMPLIS offers LuminusLive™ for an understanding of medications, their interactions and genetic influences in addition to a portal for virtual medication changes which can be analyzed in a matter of minutes. Co-existing morbidities can be efficiently treated while reducing risk to the patient for ADRs, Anti-cholinergic burden, Life style implications and genetic influences with up to the minute recommendations based on twice-daily scraping of over 6000 entries performed by Artificial Intelligence with respect to each tested genetic pathway and over 36,000 medications, herbals and OTC products along with current live-market pricing of each medication considered.
- Agomelatine(Valdoxan®)
- Amitriptyline (Elavil®)
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin®)
- Citalopram(Celexa®)
- Clomipramine (Anafranil®)
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta®)
- Desvenlaxafine (Pristiq®)
- Escitalopram (Lexapro®)
- Fluoxetine (Prozac®)
- Fluvoxamine (Luvox®)
|
- Levomilnacipran (Fetzima®)
- Mirtazapine (Remeron®)
- Nortriptyline (Pamelor®)
- Paroxetine (Paxil®)
- Reboxetine (Edronax®)
- Sertraline (Zoloft®)
- Trazadone (Desyrel®)
- Venlafaxine (Effexor®)
- Vilazodone (Viibryd®)
- Vortioxetine(Trintellix®)
|
- Improved Antidepressant Remission in Major Depression via a Pharmacokinetic Pathway Polygene Pharmacogenetic Report. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2015;13(2):150-6.
- Bousman, C. A., Müller, D. J., Ng, C. H., Byron, K., Berk, M., & Singh, A. B. (2016). Concordance between actual and pharmacogenetic predicted desvenlafaxine dose needed to achieve remission in major depressive disorder: a 10-week open-label study. Pharmacogenetics and genomics, 27(1), 1-6.
SSRI Antidepressants3
Drug Class Description:
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are prescribed to treat various psychiatric conditions, including depression, anxiety and personality disorders. SSRIs act by blocking the serotonin (5-HT) receptors in the brain. Suboptimal responses can delay the use of effective medications and remission of symptoms. Genetic differences can play an important role in determining patient responses.
- Citalopram
- Escitalopram
- Fluoxetine
- Fluvoxamine
|
- Paroxetine
- Sertraline
- Vilazodone
|
3 Please visit http://www.pharmgkb.org for full list of pathways
SNRI Antidepressants3
Drug Class Description:
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) such as duloxetine, levomilnacipran and venlafaxine are primarily indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Some SNRIs are also prescribed to treat anxiety disorders and neuropathic pain. SNRIs, like SSRIs, are second-generation antidepressants that are better tolerated than first-generation antidepressants such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
- Duloxetine
- Levomilnacipran
- Venlafaxine
|
3 Please visit http://www.pharmgkb.org for full list of pathways
TCA Antidepressants3
Drug Class Description:
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are prescribed to treat depression and various other psychiatric conditions. TCAs act by blocking the neuronal uptake of norepinephrine and serotonin; the binding of TCAs to cholinergic, alpha-adrenergic, serotonin and histamine receptors contributes to various side effects.
- Amitriptyline
- Clomipramine
- Desipramine
- Doxepin
|
- Imipramine
- Nortriptyline
- Protriptyline
- Trimipramine
|
3 Please visit http://www.pharmgkb.org for full list of pathways
Other Antidepressants3
Drug Class Description:
Other antidepressants that are used to treat depression and anxiety disorders include: Bupropion - a norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) and a non-competitive antagonist of the nicotine receptors; Buspirone – an anti-anxiety medication unrelated to benzodiazepines; Mirtazapine - a commonly prescribed second-generation tetracyclic antidepressant that inhibits adrenergic alpha2-autoreceptors and serotonin 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors; nefazodone - a phenylpiperazine antidepressant not related to SSRIs, TCAs and monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and blocks the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors; trazodone - a serotonin antagonist and a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SARI) related to nefazodone; vortioxetine - a multimodal antidepressant that can be a useful alternative to serotonergic antidepressants for some patients who are partial responders or non-responders.
- Bupropion
- Buspirone
- Mirtazapine
|
- Nefazodone
- Trazodone
- Vortioxetine
|
3 Please visit http://www.pharmgkb.org for full list of pathways